Got pointed to this paper by Sofia Ahsanuddin of the MetaSub project and thought it might be of interest.
Abstract:
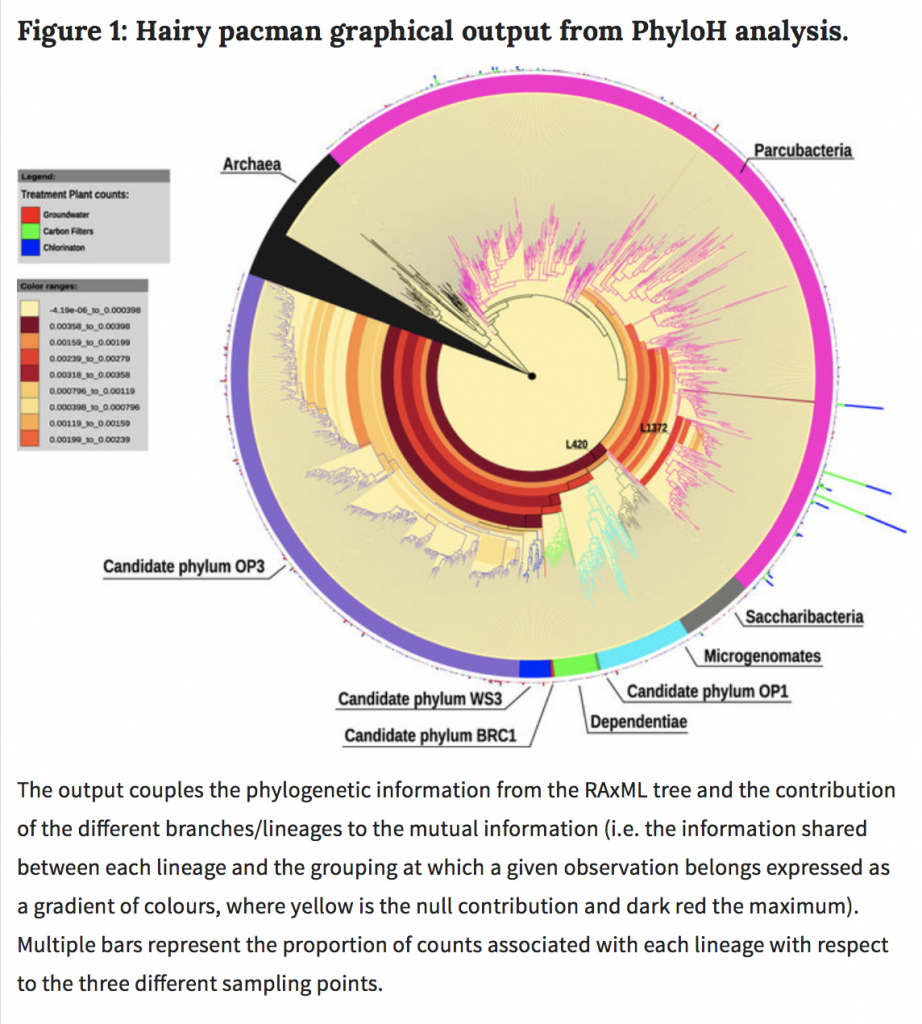
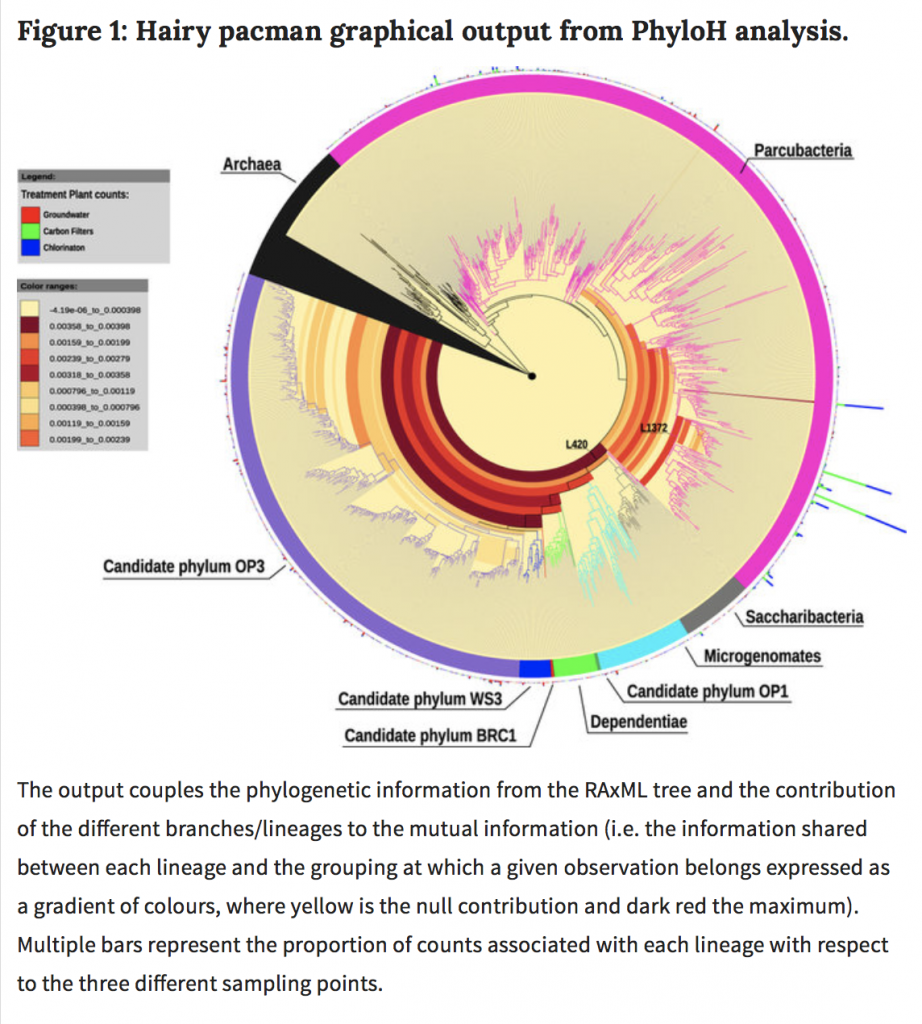
Scientists recently reported the unexpected detection of unknown or poorly studied bacterial diversity in groundwater. The ability to uncover this neglected biodiversity mainly derives from technical improvements, and the term “microbial dark matter” was used to group taxa poorly investigated and not necessarily monophyletic. We focused on such under-investigated microbial dark matter of drinking water treatment plant from groundwater, across carbon filters, to post-chlorination. We tackled this topic using an integrated approach where the efficacy of stringent water filtration (10000 MWCO) in recovering even the smallest environmental microorganisms was coupled with high-throughput DNA sequencing to depict an informative spectrum of the neglected microbial diversity. Our results revealed that the composition of bacterial communities varies across the plant system: Parcubacteria (OD1) superphylum is found mainly in treated water, while groundwater has the highest heterogeneity, encompassing non-OD1 candidate phyla (Microgenomates, Saccharibacteria, Dependentiae, OP3, OP1, BRC1, WS3). Carbon filters probably act as substrate for microorganism growth and contribute to seeding water downstream, since chlorination does not modify the incoming bacterial community. New questions arise about the role of microbial dark matter in drinking water. Indeed, our results suggest that these bacteria might play a central role in the microbial dynamics of drinking water.
It its a pretty simple paper but it highlights how little we know about the diversity of microbes on this planet, even the ones that we interact with in various ways. This paper focuses on so called “microbial dark matter” – which they define in the following sentence:
Adopting the definition of Solden and colleagues3, those microorganisms accounting for a large proportion of life and biodiversity but whose basic metabolic and ecological properties are not known are called microbial dark matter.
So they set out to characterize microbial dark matter in drinking water treatment plants. The results are summarized largely in what may be one of the best Figure titles I have seen in a long time:
Anyway – the paper is worth a look if you have an interest in the presence of very novel microbes right around us.