So – we have been having a running discussion with people in my lab about one key issue in microbiome studies – how does one store samples prior to doing DNA extractions and does it matter? As background for those who do not do this kind of work – the general principle behind DNA based analysis of microbes and microbial communities is that you can go to a sample (soil, water, air, tissue, etc) and extract DNA from that sample and then study the microbes in the sample by looking at the DNA.
This can be represented in the following cartoon:
But one of the challenges is, it is not always possible or ideal to directly isolate DNA from ones sample. And how samples are processed can affect what DNA comes out the other end and thus can affect results.
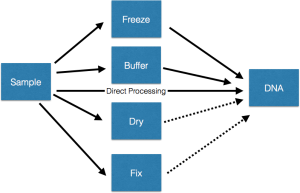
From a simple examination of a set of projects, it seems to me there are something like five main classes of approaches used in going from sample to DNA which I represent in this cartoon. Some details are in the text below.
- Freeze. Collect samples, whatever they may be (soil, swabs, tissue, etc) and freeze them, preferably at a very cold temperature. Then, when it is time to do DNA extractions, thaw them out and extract DNA.
- Buffer. Mix with some buffer or DNA stabilization / extraction solution and then let sit, possibly at room temperature, for an extended period of time. Then extract DNA.
- Process. Process fresh samples immediately (or as rapidly as possible) and extract DNA and then store the DNA for later use.
- Dry. Collect samples and dry them and then store them dried. This is done usually in cases where the main goals do not involve DNA analysis. But sometimes people would like to go to the samples afterwards and try to study microbes in and on the samples.
- Fix. Collect samples and then mix them with some sort of fixative (e.g., formalin, alcohol). This is done with all sorts of samples where the main goal is to do something other than DNA analysis. But then, after the fact, many people would like to get DNA out of these samples.
Of course, this is a bit of an oversimplification, but to me these seem to be the main categories of what is commonly done with samples. There are also other “minor” categories of what is done with samples but these five seem to cover most cases.
I am writing this post for three main reasons.
First, I would like to generate a community discussion around what people do with their samples and why. For example, I was told recently that there is some literature indicating the freezing fecal samples directly (rather than putting in some buffer) is less than ideal because the microbiomes retrieved from such samples change over time.
Second, I would like this to serve in a way as a place for people to ask questions about recommendations for what to do for their samples. For example, I got asked yesterday about how to collect plant leaf samples in the field for microbiome studies if one does not have access to a freezer.
Third, I would like to use this as a launching pad for starting to collect together formal protocols that people use in microbiome and microbiology of the built environment studies. We may use Protocols for this, but am still experimenting on systems.
So please -anyone who works on microbiome studies – we would welcome comments about methods and best practices and references and any other detail you can provide.
We wrote a paper awhile back that addressed some of these questions:
http://fiererlab.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Lauber_etal_FEMS_2010.pdf
Brilliant – very helpful.
For our cave samples our current protocol is this:
Backpack cooler load with dry ice and space blankets
Gather the samples in sterilized (inside and out) falcon tubes
Wrap in dry ice and space blankets then place inside the backpack cooler
On return to basecamp the tubes go into a better cooler with lots of dry ice
Keep frozen until processing
So – no buffer of any kind?
2014 paper from PLOS ONE Optimized Cryopreservation of Mixed Microbial Communities for Conserved Functionality and Diversity (http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0099517). Saw/heard Dr. Van de Wiele speak last year about mixed microbial communities throughout different regions of the gut; great speaker and interesting systems.
Just found this interesting paper: Evaluation of methods to purify virus-like particles for metagenomic sequencing of intestinal viromes http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/s12864-014-1207-4.pdf in BMC Genomics from Kleiner et al.
We’ve always processed human faeces as soon as it’s collected for DNA extraction. Though my colleagues and I acknowledge we’re fortunate to have access to a clinical unit and good anaerobic facilites to allow transport of samples to the lab within 1-2 hours if produced at a subject’s home. The reason we process fresh faeces for DNA extraction is because when we did a lot of FISH work, we found that a month of freezing caused big losses in Gram-negatives, especially Bacteroidales. We wanted our DNA- and FISH-based work to be as comparable as possible. We found storing aliquots of homogenate in PBS/glycerol (50:50, v/v) was better than storing 1-2 g portions of faeces for recovery of DNA and diversity. By far the biggest factor that we’ve found to affect diversity studies is the extraction method used. Kits don’t even come close to the efficiency of old-school phenol/chloroform. Consequently, for samples collected from in vitro work, we’ll still go with the old-school method. For human studies, in which we tend to have large numbers of samples, we use FastDNA kits. Gave up with Qiagen kits long ago.
thanks – this is really helpful – I am a bit worried about all the people saying they are creating “fecal sample banks” for later analysis when what they do is just freeze the samples
I’m with you on that one.
We surveyed a variety of preservation buffers and room temperature storage vs freezing dry for proteins from cyanos. We found salt+EDTA works very well. We’ve been applying it to environmental metaproteomes as well. Although the salts are a pain to clean up, so if one can freeze quickly that makes extraction easier.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3209654/#!po=0.318471
I constructed a storify about a conversation on Twitter regarding just this topic:
https://storify.com/DrJCThrash/favorite-nucleic-acid-extraction-methods
Sorry, wrong one- this is the Storify on storage methods….
https://storify.com/DrJCThrash/storing-nucleic-acids-for-a-week-w-o-a-freezer
Freeze with protecting and you will lose Bacteroides:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24161897
I think you have unintentionally misrepresented the paper.
“Samples frozen with and without glycerol as cryoprotectant indicated a major loss of Bacteroidetes in unprotected samples, resulting in higher proportions of Firmicutes.”
Thanks for starting the important discussion on Best practices for sample processing and storage prior to microbiome DNA analysis freeze? buffer? process? Lesley has made an important observation that a month of freezing of faeces caused big losses in Gram-negatives, especially Bacteroidales. Is this data published.
One of the major problems faced by us using human faeces is that the extracted DNA using the Qiagen kit yielde highly fragmented DNA of 1Kb size or less. Any suggestions? Phenol/chloroform method yielded higher concentrations but yet fragmented.
We have not published our assessment work, and have no intention of doing so. Colleagues at the Rowett Institute recently published on loss of Bacteroidetes in unprotected samples (not faeces). Regarding DNA extraction, we’ve never had problems with fragmentation with kits or phenol/chloroform methods. Where possible we have avoid vortexing, preparing to mix samples by pipetting.
Rowett paper: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/24161897/?i=4&from=mckain,%20wallace%20rj
Qiagen stool mini kit uses chemical way to lyze. The resulted DNA should not be highly fragmented. I have used a protocol from JGI to produce long DNA:
http://1ofdmq2n8tc36m6i46scovo2e.wpengine.netdna-cdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/JGI-Bacterial-DNA-isolation-CTAB-Protocol-2012.pdf
But it is a one-day-long protocol for a small number of samples.
Qiagen stool kit should be a good and easy way to get long DNAs, but it will bias greatly towards Gram negative bacteria, because it is difficult to lyze Gram+ with chemicals alone.
Bead bashing has less bias, but cannot generate very long DNA. It depends on how long DNA you need.
Very interesting and educational! Thanks! Greets, Storage Primrosehill Ltd.
I am working on a disposable sterile device designed to produce a homogenized sample within an encapsulated anaerobic environment. I’d be interested in collaborating with interested parties.
Chris, Are you still interested in collaborating for your new device??
This paper has evaluated some of the DNA preservation reagents/kits.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22974342
Very helpful discussions. I want to carry out gut microbiome analysis and was wondering on the best way to preserve my stool samples
The best way is to use a preservative. Some are available commercially.
Norgen Biotek Corp.
https://norgenbiotek.com/product/stool-nucleic-acid-collection-and-preservation-tubes
Small tubes (2ml) and larger (30 ml) tubes with preservative already aliquoted.
I hope that helps
Just saw this new paper which is of relevance to this post: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167701215001104
Effect of preservation method on spider monkey (Ateles geoffroyi) fecal microbiota over 8 weeks.
Summary from the paper below:
Highlights
• We examine differences in microbial communities due to fecal preservation method.
• Fresh, frozen, and ethanol-preserved samples have most similar microbial communities.
• 8 weeks of preservation had little effect on microbial composition and diversity.
• DNA amount/purity did not correlate to microbe amplification, diversity, and composition.
• Preservation methods exhibit bias toward/against some bacterial phyla.
Abstract
Studies of the gut microbiome have become increasingly common with recent technological advances. Gut microbes play an important role in human and animal health, and gut microbiome analysis holds great potential for evaluating health in wildlife, as microbiota can be assessed from non-invasively collected fecal samples. However, many common fecal preservation protocols (e.g. freezing at − 80 °C) are not suitable for field conditions, or have not been tested for long-term (greater than 2 weeks) storage. In this study, we collected fresh fecal samples from captive spider monkeys (Ateles geoffroyi) at the Columbian Park Zoo (Lafayette, IN, USA). The samples were pooled, homogenized, and preserved for up to 8 weeks prior to DNA extraction and sequencing. Preservation methods included: freezing at − 20 °C, freezing at − 80 °C, immersion in 100% ethanol, application to FTA cards, and immersion in RNAlater. At 0 (fresh), 1, 2, 4, and 8 weeks from fecal collection, DNA was extracted and microbial DNA was amplified and sequenced. DNA concentration, purity, microbial diversity, and microbial composition were compared across all methods and time points. DNA concentration and purity did not correlate with microbial diversity or composition. Microbial composition of frozen and ethanol samples were most similar to fresh samples. FTA card and RNAlater-preserved samples had the least similar microbial composition and abundance compared to fresh samples. Microbial composition and diversity were relatively stable over time within each preservation method. Based on these results, if freezers are not available, we recommend preserving fecal samples in ethanol (for up to 8 weeks) prior to microbial extraction and analysis.
See work from John Wallace’s group on glycerol as a cryo-protectant:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24161897
I think it is very important to consider what are the natural conditions of the sample. Feces arise from warm, anaerobic situations and thus may be difficult to stabilize.
In contrast, our samples were dry sand from coastal sand dunes. We considered storing dry at room temperature but instead opted for storing on ice in a cooler during the day in the field and that evening popping them directly into the -80C freezer until DNA extraction by bead beating three weeks later, using standard MolBio protocol a recommended by Noah Fierer.
If the sand had been damp, we probably would have stored on ice in cooler in the field and then prioritized immediate extraction, so as to skip the freezing. Soils with more organic matter (lower bulk density) might require a similar treatment, although I might try to mimic natural soil temperatures during interim storage in the field.
I tested sample preservation (buffers (SLB and GIT) and freezing in liquid nitrogen in the field) and DNA extraction methods for a wide variety of hot spring samples (pH range ~2-9). The outcome metric was detected richness (measured by DGGE, this was back in the dark days). SLB preserved samples stored at ambient temperature for up to 2 weeks then -80, extracted with a hot CTAB/SDS method was the winner, though SLB and Mobio kit was a close second.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18633656
Sorry it’s not open access, contact me and I’m happy to send on a reprint.
Kendra – can you post the PDF on a website somewhere?
Sorry, just stumbled on this blog post again. Here’s my comparison http://www.unm.edu/~kmaas/Mitchell2008_methods.pdf
We just published a paper on the stability of the fecal microbiome under different transport and storage conditions:
http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0126685
nice paper …
Just saw a new paper on this topic
Methods for Improving Human Gut Microbiome Data by Reducing Variability through Sample Processing and Storage of Stool. http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0134802
Gut microbiome community analysis is used to understand many diseases like inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Sampling methods are an important consideration for human microbiome research, yet are not emphasized in many studies. In this study, we demonstrate that the preparation, handling, and storage of human faeces are critical processes that alter the outcomes of downstream DNA-based bacterial community analyses via qPCR. We found that stool subsampling resulted in large variability of gut microbiome data due to different microenvironments harbouring various taxa within an individual stool. However, we reduced intra-sample variability by homogenizing the entire stool sample in liquid nitrogen and subsampling from the resulting crushed powder prior to DNA extraction. We experimentally determined that the bacterial taxa varied with room temperature storage beyond 15 minutes and beyond three days storage in a domestic frost-free freezer. While freeze thawing only had an effect on bacterial taxa abundance beyond four cycles, the use of samples stored in RNAlater should be avoided as overall DNA yields were reduced as well as the detection of bacterial taxa. Overall we provide solutions for processing and storing human stool samples that reduce variability of microbiome data. We recommend that stool is frozen within 15 minutes of being defecated, stored in a domestic frost-free freezer for less than three days, and homogenized prior to DNA extraction. Adoption of these simple protocols will have a significant and positive impact on future human microbiome research.
Hello,
Our company is looking for the DNA sample kit to obtain the sample and send it to a storage facility for 2.5 years. Can your company provide such service? I understand there are some restrictions/requirements/standards to take the sample.
Although our company is located in Honduras, it has access to the USPS to receive the kit and send the sample to USA. Our company also has a Plant Physician to take the sample.
Thanks in advance
hello, I do enjoy reading this blog and it has been very helpful.
However, is there any methods in preserving any perishable food items like milk products for any prolong future meta-genomic analysis?
Hello, I enjoy reading this blog and it has been very helpful.
However, is there any preservation methods that can be used for perishable items like milk products for later meta-genomic analysis?
Thank you for the informative post. I am looking to perform FISH on dental plaque samples to be transported from the field. Any suggestions will be helpful!
Hi everyone ! I had some raw materials, Curculionidae, using for dna extraction. However, after storing in alcohol 70% for 2 weeks they gave such a bad result, not much DNA. Is there any solution to solve this problem ?
Can you clarify a few things?
1. What do you mean by “not much DNA”?
2. Do you get more DNA from fresh samples?
3. Probably better to use 100% ethanol
4. How did you do the DNA extraction?
Hi Jonathan Eisen !
First of all, I want to say thank you for your reply !
1. Actually, I saw some weak bands.
2. Yes, I do. After having that bad result, I made another test by using fresh samples and the result was much better, no more weak bands.
3. Maybe I will try 100% ethanol :)
4. I used CTAB method.
Hello!
Thanks for providing space for discussion and I have somewhat relevant input for this subject.
My research focuses on describing gut fungal communities by combining ITS1 sequencing and phenotying cultured fungal isolates. The preliminary results from comparing fresh vs frozen (-80 C) stool sample indicates loss in fungal viability, which was not a big surprise. Because of this reason, I’m leaning towards using fresh samples for culturing efforts then freezing (-80 C) the remaining samples for DNA extraction in batches. I presume that the approach suggested by Gorzelak and colleagues (whole stool homogenization after flash freezing) would lead to significant loss of viable bacterial and fungal cells and would not be a practical method for me. Further, it would be interesting for such studies to include changes in fungal community detection in different sample storage conditions (I haven’t found any yet!).
David
Hi there! Nice blog
I am thinking in starting a project on skin microbiome and I have a very basic question. How do you sterilize the solutions and equipment for NOT having microbe DNA in/on them???? Filters, UV, autoclave, combinations or others?
Thank you!
I ran into a similar question (how to best preserve samples under field conditions without access to cold storage for weeks), so I decided to make a list of papers addressing this topic, on my MicrobiomeDigest blog. I have included all papers mentioned above, as well as several others. Here is the list:
https://microbiomedigest.com/microbiome-papers-collection/non-human-microbiome-paper-collection/sample-storage/
I hope this is helpful!
Elies
Hello all – I stumbled upon this page via Google. What a fantastic page – truly. My group’s question is more proteomic. It seems that the preservatives discussion tends toward either DNA quality or diagnostic parasitology domain. We will be performing an assay to determine the level of calprotectin in stool (human). An expert that I pinged stated that, “Fcal is biologically functional as a hetoerodimer and heterotetrimer (and this is what the assay measures), I assume the ethanol would denature the 3* and 4* structure and cause a problem.” Given that consideration, does anyone have any thoughts about the best preservative in this case?
David,
Just saw your comment and I am actually interested in validating our stool preservative for the purpose of stabilizing calprotectin. If would be open to testing this, please let me know !
Jaclyn
j.ugulini@gmail.com
A paper of interest to this topic was just published
http://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-016-0186-x
Latitude in sample handling and storage for infant faecal microbiota studies: the elephant in the room?
We just launched a buffer based microbiome sample collection and stablization device, iSWAB-Microbiome. This technology is designed to help defining the microbiome precisely from point of collection to processing, while storing and transporting the sample at ambient temperatures.
Please do not hesitate to contact me directly if you find such technology of interest to you and like to receive free samples or further information.
http://www.mawidna.com/products/iswab-microbiome/
Bassam
b.elfahmawi@mawidna.com
Hi,
Just found this great discussion. Nice to see collaboration in action. I wondered if anyone had advice on DNA extraction and preservation method for microbial communities in seawater hatcheries? My previous experience is with fish gut and skin samples but I am expecting less DNA Quantity and diversity in the hatchery samples? I am struggling to find published papers on this so any advice or guidance gratefully appreciated.
I am also interested in your question, Mags C. We are planning to build a library of samples from sea star epidermal swabs over several years, and at a future date, go back and cherry-pick samples from a time period surrounding and during disease outbreak. I am concerned about degradation (biased toward one phyla, or overall) during storage. Any advice would be appreciated.
MAGS and Marion,
I believe we can help with swab based collection and stabilization from point of collection to processing. Also, we might be able to provide a customized portable solutions. If interested in exploring this further, please feel free to contact me directly.
Hi all- stumbled upon this discussion and have read some very useful information!
I was wondering if any one has worked with viral DNA and RNA, particularly in faecal samples? I am working on characterising the gut virome of the Tasmanian devils. Most studies I have looked at store their samples in -80C. I understand RNA degrades rapidly, hence why freezing them at -80 is preferable. Since we collect samples on the field and have no access to a -80 freezer, I’m worried about degradation. Most of these samples have been kept at -20 for 2-3 weeks before arriving to our lab and moved to the -80 freezer here.
Does anyone have any experience dealing with viral DNA and RNA from stool and can recommend the best storage conditions?
Can anybody help me with information on method(s) for long term storage of soil samples such that that we can isolate much of the microbiota from it without much loss as in the freshly collected soils ?
Similar to Murali Gopal who posted above, I would be very interested in learning anyone’s opinion on how to store soil samples for the long term with the intention to conduct direct environmental DNA extraction on them later. Thanks.
You can use Stool collection & Preservation kits from Norgen Biotek. These will store the DNA for more than two years at ambient temperature. These type of transport & storage are used routinely for stool samples for mirobiome studies where the sample need freezing and in this case “Chemical freezing” and as a bonus the sample will be homogenized during storage. The preservative is compatible with various DNA isolation kits.
The DNA isolated from these samples are suitable for NGS and PCR. I hope this helps.
Nezar Rghei
ISWAB-Microbiome is designed for swab based Soil collection. Check the instructional video for further detials on the collection process, hope this helps:
hi! about storage, I would like to know if it is possible to freeze MoBio collection beads tubes in -80C. Or which method is the best to collect and storage skin microbiota.
thank you!
got some responses on Twitter – here is a Storify summary of them https://storify.com/phylogenomics/sample-preparation-summary
Hello!
We offer a system that is complete with swab and preservative for room temperature preservation of skin DNA. It will preserve skin microbiota from the point of collection, ensuring minimal biast in data anlysis downstream: https://norgenbiotek.com/product/swab-collection-and-dna-preservation-kit
Does a product exist that can swab and store DNA samples on site, without keeping sample cold, but by adding a preservative instead? The samples must be able to be transported for testing without being on ice and remain viable for long periods of time? Thank you for your thoughts.
I posted this to Twitter. And got some responses. See some of them here
https://storify.com/phylogenomics/question-on-microbenet-about-swabbing-for-dna
Yes there is, iSWAB-Microbiome is swab based sample collection that is designed to maintain the microbial community at a status quo, viable, from collection to processing (up to 8 weeks). This is why you can get microbial DNA and RNA from the same sample. Basically the after the swab is collected the content is mechanically removed from the swab head and released into the stabilizing buffer pre-dispensed in the iSWAB-Microbiome device (fecal, oral, vaginal, skin, soil, etc…), then the swab is removed and discarded. The the devcie then transported at room temperature or further processing: http://www.mawidna.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/iSWAB-MB-Protocol-v2.pdf
I hope this answers your question. Meanwhile, I will be more than happy to offer you free samples to try it out if you think this would be of help to you:
http://www.mawidna.com/sample-request/
Hi Cherrie,
We can help with that (www.norgenbiotek.com).
We have a swab system optimized for both fecal swabs and general swab applications.
Feel free to email me for more information.
Jaclyn
Hi, I’m looking for a stable protocol for soil nutrient analysis and microbiome analysis. Our window of opportunity for the field season is very short, but we’ve had a delay on our field instruments so we can’t do the nutrient testing in the field for all of our sites. I wanted to be able to store part of the soil for the microbiome analysis and parts for nurtient analysis. Does anyone know compatible protocols/storage methods for either of these?
Hi Kelli,
We just finalized the development of iSWAB-MicrobeOmics for room temperature collection and storage (not launched yet, in beta now). This is specifically designed tfor applications like yours in order to stabilize microbial nucleic acids and metabolites including minerals from pointof collection to processing. We will be more than happy to offer you samples and or collaborate with you on this project. You can reach out directly to me at b.elfahmawi@mawidna.com and we can chat further.
Best regards,
Bassam
Thank you for your original post – interesting read. This may be the wrong forum – if so,please excuse me, and thank you for taking the time to read this.
I am curious about how your profession stores your samples before processing, and how it may relate to forensic dna samples and genetic genealogy.
My mother recently passed away and i hope to recover the dna on household items (tissues, toothbrush, dentures, hearing aid, nail clippings.)
I do not know much about dna preservation, or at what rate it degrades,and have a hard time finding out.
So far i have 3 choices:
1) DNA home banking – various labs boast they can process forensic samples and store dna in a capsule. This problem is some labs say their capsules will last 11 years , others say indefinitely. Can a lab truly store the dna indefinitely by desiccation?
2) Forensic sample storage – I was told that i could store the items in paper envelopes in a controlled environment for some years at home in the hopes technology will improve and i can get a better chance of recovering the dna. Is this correct? How would i create a controlled environment that will last for years?
3) Process ASAP – I have the option of sending the items off to a lab to be processed, however the success rate is 60 to 90%. If option 1 & 2 above aren’t viable, is this the best choice?
thanks again.
I posted this to twitter and there are some responses there. See https://twitter.com/phylogenomics/status/922469220624957440
Please check out iSWAB-Microbiome collection technology from MAWI DNA Technologies that can address all your concerns. Below is a recent press release of our product validation work with CosmosID:
https://mawidna.com/uncategorized/mawi-and-cosmosid-collaborate-to-enable-more-precise-microbiome-analysis/
Will be more than happy to offer free samples for your hands on evaluation!
https://mawidna.com/sample-request/
So hopfully this thread is still up to date.
If got a few questions after reading several of papers on stool collecting and DNA extraction methods.
1. Question: does extended storage/collection constrains extraction-is there any study??
2. Question: is it possible to extract DNA from RT in a maximally compatible way to what one can do with freezing
3. Question: what sampling and extraction methods can be combined.
Thank you all for the help